ArrayList源码解析之subList
ArrayList的 subList ( int fromIndex, int toIndex ) 方法执行结果是获取ArrayList的一部分,返回的是ArrayList的部分视图。《阿里巴巴Java开发手册》中对subList方法的使用有规定: 首先通过一个例子,初步了解subList的用法和易出错的地方:
首先通过一个例子,初步了解subList的用法和易出错的地方:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class SubListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
System.out.println("原:" + list);
List<Integer> subList = list.subList(0, 5);
System.out.println("子:" + subList);
// subList的add()方法
subList.add(3, 21);
// 输出原集合
System.out.println("==============subList的add()方法执行结果====================");
System.out.println("原:" + list);
// 输出subList
System.out.println("子:" + subList);
// ArrayList的add()方法
list.add(31);
// 输出原集合
System.out.println("==============ArrayList的add()方法执行结果====================");
System.out.println("原:" + list);
// 输出subList
System.out.println("子:" + subList);
}
}
程序的执行结果为: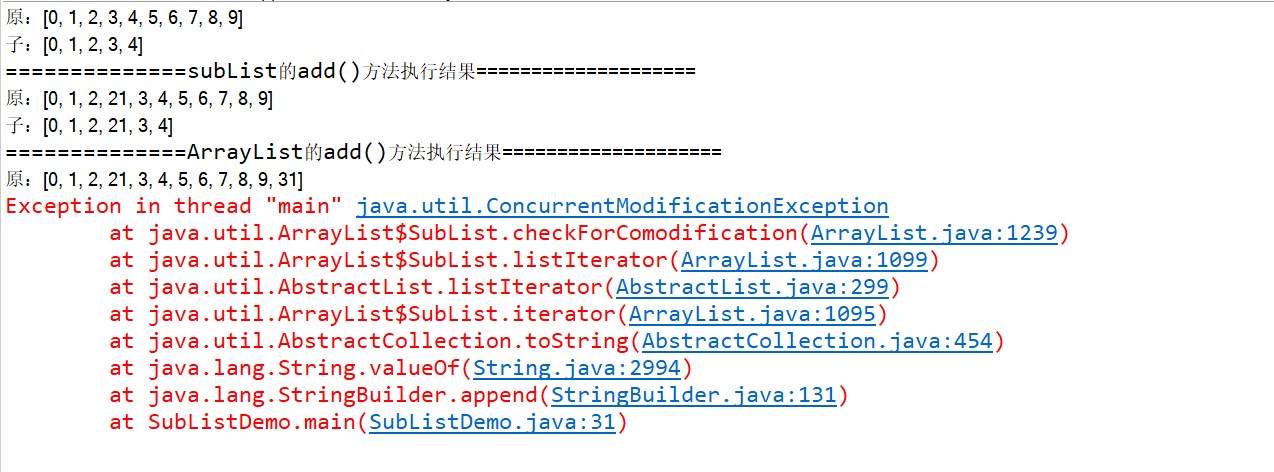 从结果得出:
从结果得出:
- 对子类subList的操作会反映到父类中。
- 使用父类的方法(能改变modCount值的方法)修改集合会导致子类的遍历抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。
程序的执行结果也验证了阿里手册的规定,下面,通过源码解析更加清晰的理解这两条规定的用意。
ArrayList 的 subList 方法返回的一个内部类 SubList,返回的 List 中,下标范围在[fromIndex, toIndex) 之间:1
2
3
4
5
6public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
// 参数检查
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
// 内部类SubList,this为父类的引用,0 表示父类下标偏移量
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);方法检查两个下标是否合规:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
SubList 内部类,继承了 AbstractList 类,并实现了 RandomAccess 接口,支持随机读取:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266/*
* SubList返回的视图是由父类集合支持的,因此是非结构化的
* 所以,对SubList子集合进行操作,也会修改父类的集合。
* SubList类中,每个public方法(除了subList()方法)都调用checkForComodification()
* 用于判断父类集合是否被修改
* 所以,如果直接使用父类方法修改父类集合,则SubList子类的遍历、增加、删除等操作都会抛出异常
*/
private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {
// 父类的引用
private final AbstractList<E> parent;
/*
* 父类集合中的位置,如果使用SubList中的subList方法,
* 则此时父类为SubList类,不是ArrayList
*/
private final int parentOffset;
// 子类List在父类 ArrayList 中的下标位置
private final int offset;
// 视图集合的size
int size;
// 构造方法,参数offset表示父类集合的下标偏移量
SubList(AbstractList<E> parent,
int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.parent = parent;
this.parentOffset = fromIndex;
this.offset = offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E e) {
// 检查下标是否越界,这里index的值在[0, this.size)之间,size = toIndex - fromIndex
rangeCheck(index);
// 检查是否有其他线程修改了父类集合
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
// 调用父类方法替换元素,所以本质上还是在父类集合中替换元素
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e;
return oldValue;
}
public E get(int index) {
// 检查下标是否越界,这里index的值在[0, this.size)之间
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
// 调用父类方法获取元素
return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return this.size;
}
public void add(int index, E e) {
// 检查下标,index的值在[0, this.size]之间
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
// 使用父类方法添加元素,下标位置为parentOffset + index, 在父类集合添加元素。
parent.add(parentOffset + index, e);
// 父类add()方法修改了modCount的值,更新subList的modCount值
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size++;
}
// 根据下标移除元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size--;
return result;
}
// 移除指定区间的元素
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex,
parentOffset + toIndex);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size += cSize;
return true;
}
// subList 中迭代器使用ListIterator(),迭代器的源码已分析
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
final int offset = this.offset;
return new ListIterator<E>() {
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
}
("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
// offset + index 的下标为此时subList中元素在父类集合中的位置
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = SubList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[offset + (i++)]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
// 与 Itr 中不同
lastRet = cursor = i;
checkForComodification();
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 检查是否有多线程修改集合
final void checkForComodification() {
if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
}
// 内部方法
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
// 下标越界检查
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
// 下标越界检查,仅add()方法和addAll()方法使用
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
// 下标越界异常信息
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
}
// 是否有多线程修改集合
private void checkForComodification() {
if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// 下篇文章讲解
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
checkForComodification();
return new ArrayListSpliterator<E>(ArrayList.this, offset,
offset + this.size, this.modCount);
}
}
关于 parentOffset 和 offset :