ArrayList源码解析之remove,removeIf
remove() 方法用于删除集合中的元素,本篇主要解析ArrayList的remove(),removeAll(),以及JDK1.8中新增的removeIf()方法。
一、remove()
remove()方法有两个:
1、删除集合中指定位置元素的 remove(int index) 方法。
2、删除指定的、在集合正序遍历中第一次出现元素的 remove(Object o) 方法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50// 根据下标删除元素
public E remove(int index) {
// 检查下标是否越界
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
// 需要移动元素的个数
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 将elementData数组index+1位置(包含index+1)以后numMoved个元素向前移动一位
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
// 删除指定的、在正序遍历中第一次出现的元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
// 删除数据方法
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* 与remove(int index)方法差异在于该方法不用检测下标是否越界
* 虽然没有下标越界检查,但index的取值范围为 0 <= index < size
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
二、removeAll()
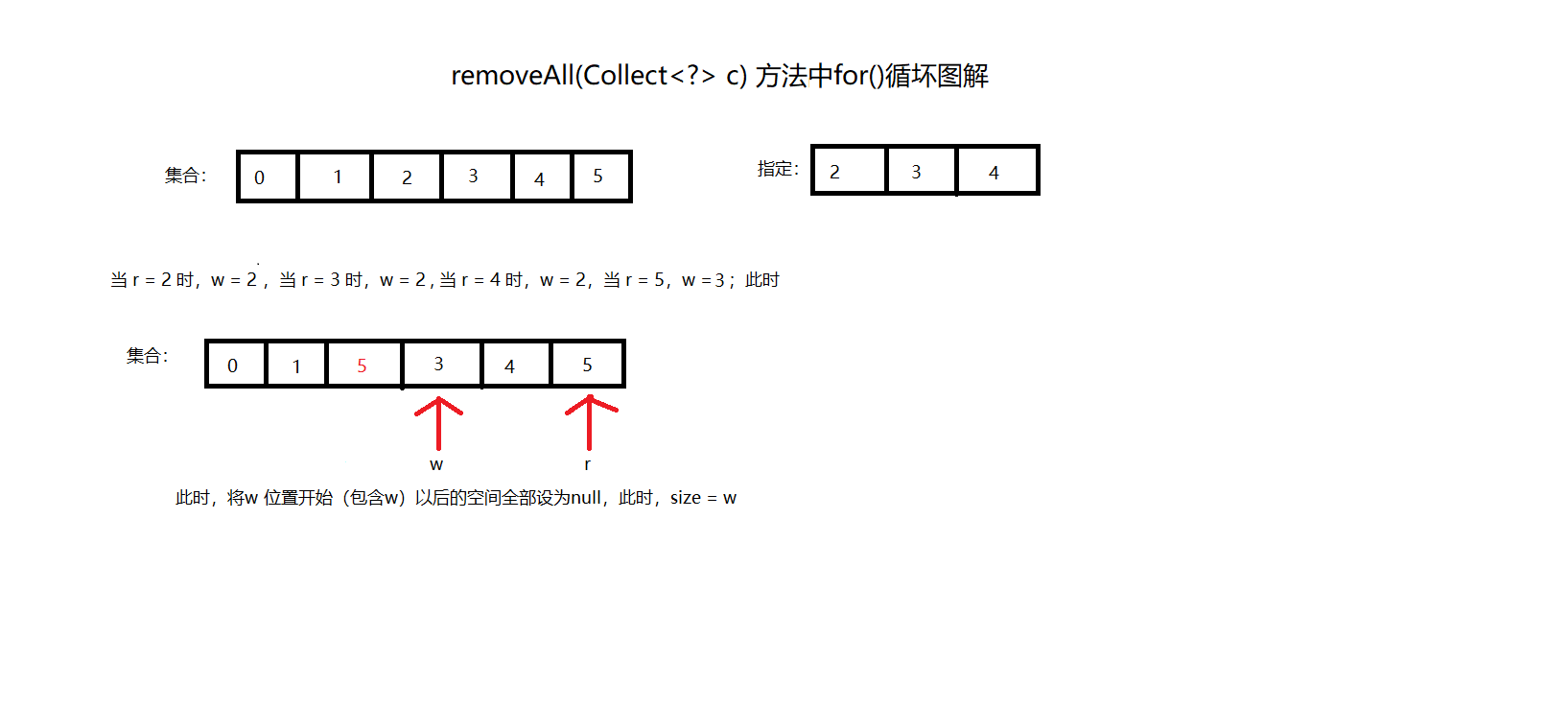
removeAll(Collect<?> c) 删除集合中所有在目标集合c中存在的元素,主要方法为私有batchRemove()方法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0, w = 0;
// 执行结果
boolean modified = false;
try {
/*
* 如果目标c中包含elementData[]中的元素
* 则用此时r位置的元素(不存在c集合)替换w位置的元素(存在c中)
* 可见图一
*/
for (; r < size; r++)
// boolean complement = false
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
/*
* 如果for循环执行过程中,contains()方法抛出异常
* 此时需要整理elementData数组
* 将抛出异常时r位置(包含r)以后的元素全部向前移动r-w位
*/
if (r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
elementData, w,
size - r);
// 此时集合size值
w += size - r;
}
/*
* 如果无异常抛出,w下标(包含w)以后的元素,都已被复制到w下标之前
* 之后的元素做null值处理
*/
if (w != size) {
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
// 移除成功后,w为此时的size
size = w;
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
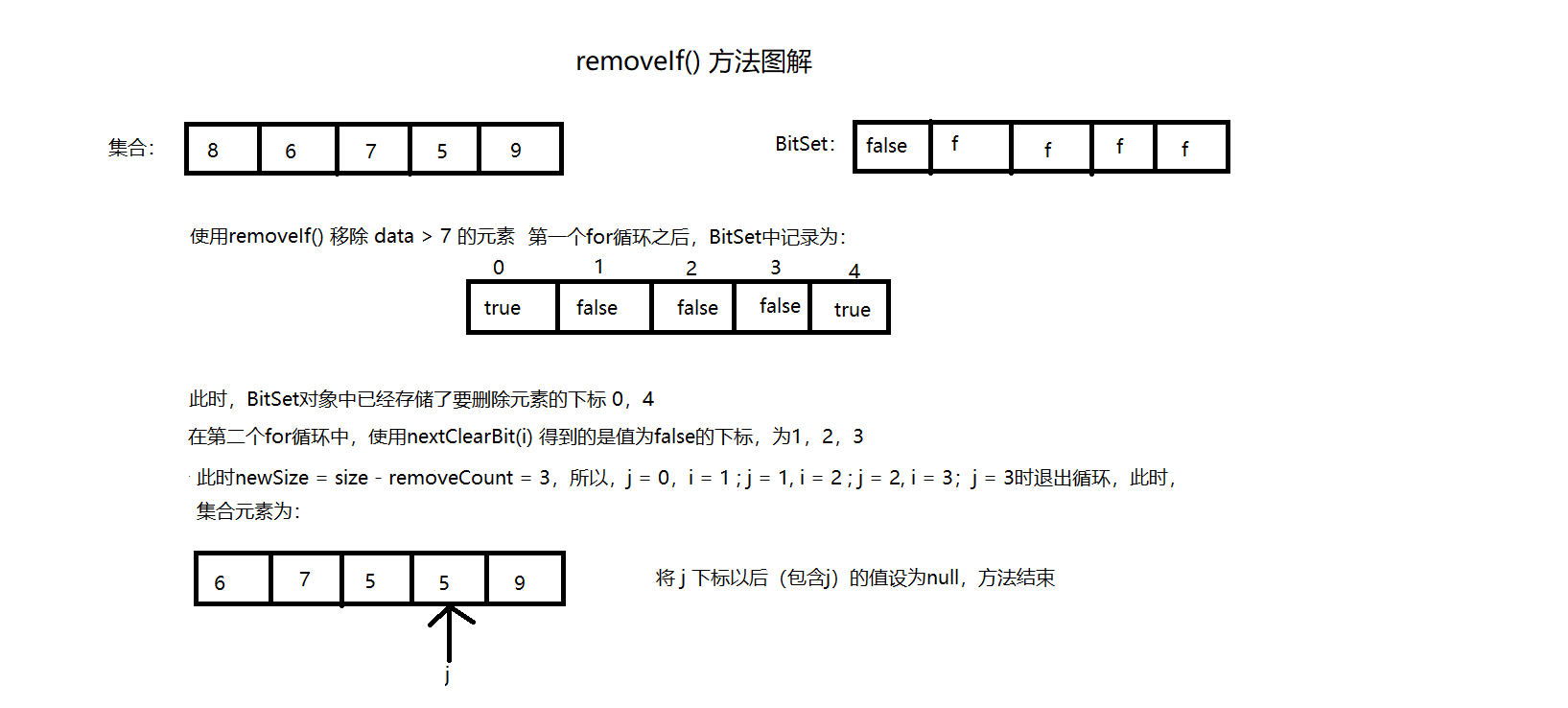
三、removeIf()
removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter)方法是JDK1.8新增方法,作用是按照一定的规则过滤集合中的元素,示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20import java.util.ArrayList;
public class RemoveIfDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 移除大于5的元素
list.removeIf(it -> it > 5);
System.out.println(list);
// [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
}
源码解析1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63/*
* JDK1.8新增方法,作用是按照一定的规律过滤集合中的元素
*/
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
// 判断参数是否为空
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
// figure out which elements are to be removed
// any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage
// will leave the collection unmodified
// 满足一定规则元素的个数
int removeCount = 0;
// 使用BitSet对象记录要移除元素的下标
final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
("unchecked")
final E element = (E) elementData[i];
// 如果集合元素满足指定的规则,则将BitSet中对应下标位置的值设为true
if (filter.test(element)) {
removeSet.set(i);
removeCount++;
}
}
// 检查是否有其他线程对集合进行了修改
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements
final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;
if (anyToRemove) {
// 过滤之后集合新的size
final int newSize = size - removeCount;
// 循坏的目的在于移除满足规则的元素
for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {
/*
* nextClearBit(int index)返回设置为false的第一个位置的索引
* 发生在指定的起始索引之后。
* 如果集合元素为[0,1,2,3,4],BitSet中存储需要移除的下标为[1,3]
* 则在for循坏中 i = nextClearBit(i)返回的i值为0 2 4
* 所以此时i表示不符合规则元素的下标
* 可见图二
*/
i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);
elementData[j] = elementData[i];
}
// 从newSize(包含newSize)的下标开始,以后的值设为null
for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {
elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
this.size = newSize;
// 检查是否有其他线程对集合进行修改
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
return anyToRemove;
}